
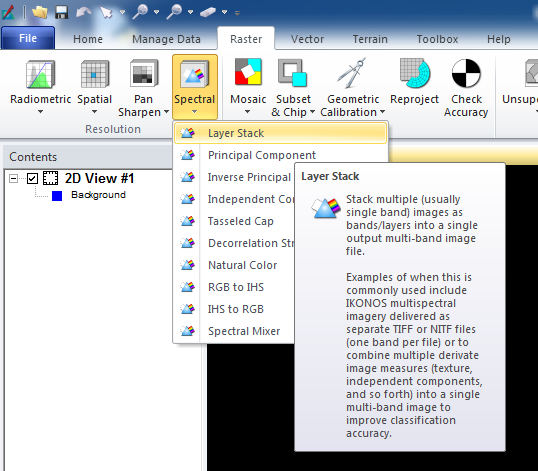
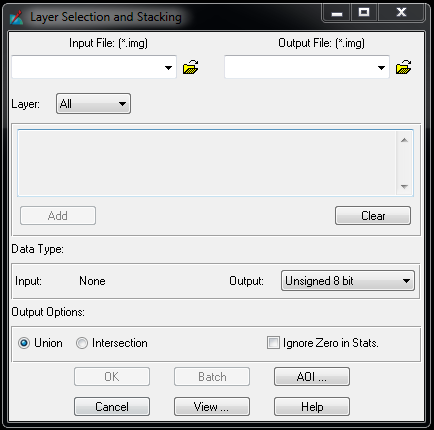
With three bars and the arrow (5th symbol in the tool bar) (merge selected signatures) to combine all the samples.Ī new class should appear which a combination of all the samples collected. This will highlight all of the samples in a single class just created and then click on the button.Click and hold on class 1, which is under the column ‘Class #’, and move the mouse down to the end of one class and then release.After all pixels in the input image have been categorized, the results are presented in the output stage. If the pixel is insufficiently similar to any training data set, it is usually labeled ‘unknown’. In classification, each pixel in the image data set is categorized into the land cover class it most closely resembles. Once the preferable numbers of sample is selected the Signature Editor window should look like the image below. Repeat the steps as water for rest of the classes (vegetation, grassland). Increase in number of samples (AOI layer), will increase the accuracy of classification.ĩ. Repeat steps 5,6 and 7 for the rest of water. Bring up the Signature Editor window and click on the button with a + sign and an arrow (+ ) (Create new Signature(s) from AOI.An AOI (Area of Interest) layer is formed. These do not have to be large polygons but make sure that all the pixels within the polygon are of water. Click once within the water to start the polygon and then keep clicking to draw a polygon. Now go back up to the top of the screen and click on Drawing tab → Polygon Icon.Click on Raster tab → Supervised → Signature Editor.Ī new ‘Signature Editor’ window will open. To change bands: Multispectral → set layer- 3, 2, 1.Ĥ. Subset the area of interest and change bands (True colour to False colour). Open satellite image (‘satdec.img’ (Landsat 8 OLI)) image in the viewer.

To yield acceptable classification results, training data must be both representative and complete. The more time and effort spent in collecting training site the better the classification results. It also requires substantial reference data and a thorough knowledge of the geographic area to which the data apply. The training stage requires close interaction between the image analyst and the image data. In this stage, the analyst identifies representative training sites/areas (i.e., a particular land cover type), then the computer determines the spectral signatures of the pixels within each training are,and uses this information to define the mean and variance of each of the classes. Accuracy assessment is required to get an accurate classification. This classification consists of three stages: Training stage, Classification stage and Output stage. In this approach, the users define useful information categories and then examine their spectral separability. In supervised classification the image analyst supervises the pixel categorization process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
